The Journey of Sugarcane: From Harvest to Everyday Products
The journey of sugarcane is a diverse process that starts with careful growing and culminates in a range of products that permeate our everyday lives. As we explore the various aspects of sugarcane's trip, its duty in sustainability and the wider effects for our environment come into sharper focus.
Cultivation of Sugarcane
The growing of sugarcane is an essential farming process that calls for certain environmental problems and administration techniques. Optimum development happens in exotic and subtropical areas where temperature levels range between 20 ° C and 32 ° C. Adequate rains or irrigation is important, as sugarcane grows in wet dirt with well-drained problems (sugarcane product). Soil quality dramatically influences return; thus, farmers typically perform soil tests to identify nutrient needs
Growing typically occurs in rows, making use of stem cuttings called setts, which are grown horizontally. This technique promotes efficient collecting and takes full advantage of sunshine exposure. Crop turning and intercropping are recommended practices to improve soil fertility and reduce insect problems. Additionally, farmers utilize incorporated pest monitoring methods to decrease chemical inputs while making certain healthy plant growth.
Timely application of these plant foods can significantly improve sugar yields. Overall, effective sugarcane cultivation pivots on a combination of environmental stewardship, tactical preparation, and continuous monitoring practices.
Gathering Techniques
Effective sugarcane growing culminates in the collecting stage, which is crucial for maximizing return and ensuring quality. The timing of the harvest is crucial; sugarcane is generally collected when sucrose levels optimal, normally in between 10 to 18 months after growing. This period differs based on climate, soil type, and sugarcane range.
Collecting methods can be broadly categorized into guidebook and mechanical methods. Hands-on harvesting is labor-intensive, counting on proficient employees who utilize machetes to reduce the stalks close to the ground. This technique enables selective harvesting, where only the ripest walking sticks are picked, therefore enhancing general sugar material.
Alternatively, mechanical harvesting has actually gained popularity because of its performance and cost-effectiveness. Specialized farmers equipped with cutting knives and conveyor systems can process big locations promptly, significantly decreasing labor expenses. This method may lead to the inclusion of immature canes and a potential decrease in sugar quality.

Despite the method employed, ensuring that collected walking canes are delivered quickly to processing facilities is essential. Motivate taking care of lessens wasting and protects the integrity of the sugarcane, establishing the phase for optimal processing.
Handling Techniques
Processing sugarcane entails numerous important steps that change the collected stalks into usable items, mostly sugar and molasses. The initial phase is washing the cane to get rid of soil and particles, complied with by the extraction of juice via crushing or milling. This process normally utilizes hefty rollers that break the cane fibers to launch the sweet fluid included within.
As soon as the juice is drawn out, it undergoes information, where impurities such as dirt particles and bagasse are gotten rid of. This is often accomplished by including lime and heating up the juice, allowing sedimentation. The cleared up juice is then concentrated via evaporation, where water web content is decreased, causing a thick syrup.
Eventually, the handling of sugarcane not only creates sugar and molasses yet also lays the groundwork for numerous derivatives, which will be checked out in succeeding discussions.
Products Derived From Sugarcane
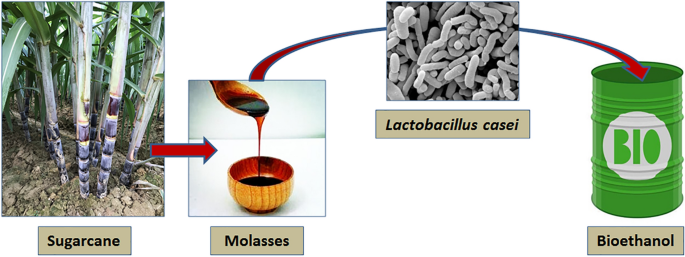
Sugarcane is a flexible plant that generates a wide range of items past simply sugar and molasses. Among the main spin-offs are ethanol and biofuels, which have actually gained importance as renewable resource sources. Ethanol, generated via the fermentation of sugarcane juice, works as an alternative to fossil fuels and is commonly combined with gasoline to create cleaner-burning fuels, decreasing greenhouse gas discharges.
Furthermore, sugarcane is a considerable resource of bagasse, the coarse deposit continuing to be after juice removal. Bagasse is learn this here now made use of in numerous applications, consisting of the manufacturing of paper, biodegradable packaging, and as a biomass fuel for energy generation. Its usage not just lowers waste but also boosts the sustainability of sugarcane handling.
Moreover, sugarcane-derived items include the food industry, where it functions as an all-natural flavor agent and sweetener in numerous cooking applications. In the realm of cosmetics, sugarcane extracts are included right into skincare products as a result of their all-natural exfoliating homes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The farming and processing of sugarcane have significant effects for ecological sustainability. This crop calls for considerable water resources, usually bring about exhaustion of local water products and impacting surrounding environments. Furthermore, the usage of plant foods and pesticides in sugarcane farming can lead to soil destruction and waterway air pollution, positioning threats to biodiversity.

Sustainable sugarcane farming likewise advertises soil health and wellness via plant rotation and minimized husbandry, enhancing carbon sequestration. The adoption of these methods not just supports environmental stability yet also improves the durability of farming areas against climate modification.
Final Thought
In recap, the trip of sugarcane encompasses different stages from growing to handling, inevitably resulting in a broad variety of items. The value of sugarcane extends beyond mere sweeteners, adding to renewable resource via ethanol manufacturing, lasting product packaging using bagasse, and natural extracts for cosmetics. This multifaceted crop plays an important duty in both dietary enrichment and environmental sustainability, highlighting its significance in contemporary agricultural and industrial practices.
Successful sugarcane cultivation culminates in the harvesting phase, which is pivotal for taking full advantage of yield and making sure high quality. The timing of the harvest is vital; sugarcane is normally collected when sucrose degrees top, typically between 10 to 18 months after planting.Handling sugarcane entails a number of important steps that transform the harvested stalks right into functional products, mainly sugar and molasses.Sugarcane is a versatile plant that produces a broad range of products past just sugar and molasses. Additionally, the usage of plant foods and pesticides in sugarcane farming can result in soil destruction and river pollution, posing threats to biodiversity.